Step into the realm of measurement with kilo definition, a fundamental concept that shapes our understanding of the metric system. From the smallest digital bits to the vast cosmic distances, the kilo prefix plays a pivotal role in quantifying our world.
Delving into its etymology and historical evolution, we unravel the significance of kilo, revealing its pervasive presence in diverse fields such as science, technology, and everyday life.
Unit of Measurement

The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is a standardized system of measurement that is used in most countries around the world. The metric system is based on the decimal system, which makes it easy to convert between different units of measurement.
One of the most common prefixes used in the metric system is the kilo prefix, which means “one thousand.”
The kilo prefix is used to denote a unit that is 1000 times larger than the base unit. For example, a kilometer is 1000 meters, a kilogram is 1000 grams, and a kiloliter is 1000 liters.
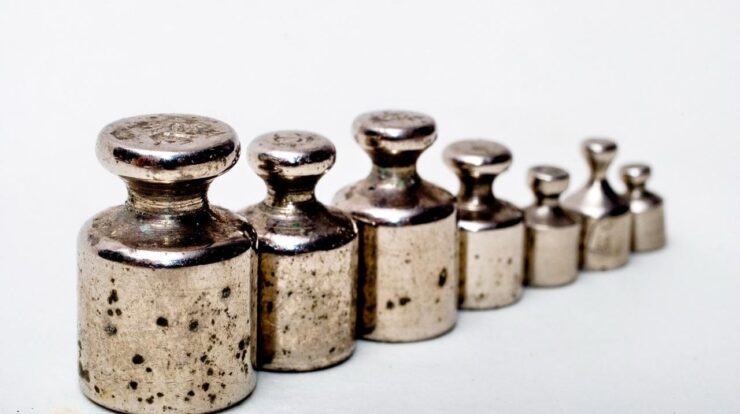
Kilogram
The kilogram is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram (IPK), a platinum-iridium cylinder that is kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) in Paris, France.
The IPK was created in 1889 and has been used as the definition of the kilogram ever since. However, the IPK is not a perfect standard, as it has been shown to lose mass over time. As a result, the BIPM is currently working on a new definition of the kilogram that is based on the Planck constant.
Kilojoule
The kilojoule (kJ) is the SI unit of energy. It is defined as the amount of energy required to move a mass of one kilogram through a distance of one meter in one second.
The kilojoule is a commonly used unit of energy in many different fields, including food science, nutrition, and engineering.
Kilobyte and Kilobit
The kilobyte (KB) and the kilobit (kb) are units of digital information. A kilobyte is equal to 1024 bytes, and a kilobit is equal to 1024 bits.
Kilobytes and kilobits are commonly used to measure the size of computer files and the amount of data that is transferred over a network.
Kilohertz and Kilohertz, Kilo definition
The kilohertz (kHz) and the kilohertz (kHz) are units of frequency. A kilohertz is equal to 1000 hertz, and a kilohertz is equal to 1000 hertz.
Kilohertz and kilohertz are commonly used to measure the frequency of electrical signals and the speed of computer processors.
Kilometer
The kilometer (km) is the SI unit of length. It is defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in one second.
The kilometer is a commonly used unit of length in many different fields, including geography, transportation, and engineering.
End of Discussion

In conclusion, kilo definition serves as a cornerstone of the metric system, enabling us to measure and compare physical quantities with precision and consistency. Its versatility extends across disciplines, facilitating scientific advancements, technological innovations, and everyday tasks.
General Inquiries: Kilo Definition
What is the origin of the kilo prefix?
The kilo prefix originates from the Greek word “khilioi,” meaning “thousand.”
How is the kilogram defined in the SI system?
The kilogram is defined as the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram, a physical artifact stored in France.
What is the difference between a kilobyte and a kilobit?
A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information equal to 1,024 bytes, while a kilobit (kb) is equal to 1,000 bits.